Why Do Stars Twinkle?
When a ray of light travels from one medium to another it ‘bends’. This phenomenon is referred to as refraction . If it travels from a rare medium to a dense medium, it bends towards the normal and if it travels from a dense medium to a rarer medium, it bends away from the normal. The speed at which the light travels changes depending on the medium and therefore this bending occurs.
This effect can be observed when light passes through a prism or a glass slab and even when light passes through water. The light ray travels from air to a medium of different densities here.
So how are refraction and twinkling connected? The atmosphere Of Earth is made of different layers. It is affected by winds, varying temperatures, and different densities as well. When light from a distant source (a star) passes through our turbulent (moving air) atmosphere, it undergoes refraction many times. When we finally perceive this light from a star, it appears to be twinkling! This is because some light rays reach us directly, and some bends away from and toward us. It happens so fast that it gives a twinkling effect.
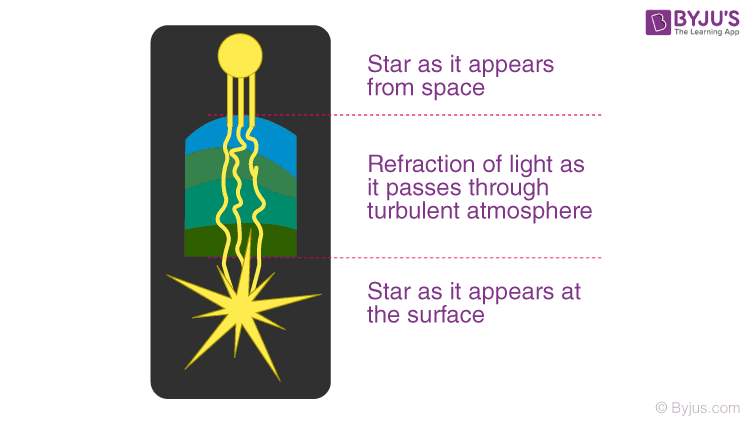
If you are in a large empty field such that the horizon is visible to you, you will notice that stars in this region appear to twinkle a lot more than stars right overhead. Why do you think this happens? Why do stars twinkle more when viewed from such places? It is because there are more layers of the atmosphere between you and the star in this direction. Therefore, more series of refractions!
Quick Summary
Why do the stars twinkle? |
As a star’s light penetrates the Earth’s atmosphere, every individual stream of starlight is refracted – caused to change direction, slightly – by the various temperature and density layers in Earth’s atmosphere. You might think of it as the light travelling a zig-zag path to our eyes, instead of the straight path the light would travel if Earth didn’t have an atmosphere. |
Don’t Planets Twinkle?
Planets are closer to us as compared to stars. Stars are very far away from us and appear as point sizes to us. Due to this, it seems as if the light is coming from one point source. On the contrary, planets are at a lesser distance from us as compared to stars. Due to this reason, they appear much more prominent, and the light seems to come from more than one point source. The dimming effect of some of the points of light coming from the planet is nullified by the brightening effect of light coming from other points.

Comments
Post a Comment